

What Is Chronic Pain Syndrome?
Chronic pain syndrome is a severe condition that can cause many problems. This guide explains the symptoms, causes, and treatment of chronic pain.
The information presented on this page is an overview of the average evaluation of chronic pain and is offered here as a resource. At J. Flowers Health Institute, our evaluations and treatment plans are customized and tailored to each individual’s needs. We specialize in providing a comprehensive team approach to your care. Our evaluations may include neuropsychological and medical testing, brain mapping, and a chronic pain assessment for help diagnosing your symptoms to provide the holistic care you deserve.
If you would like to learn more about J. Flowers Health Institute, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Table of Contents
Reach Out to Learn More
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Chronic Pain Disorders
Chronic pain affects millions of people in the United States each year. The uncomfortable and persistent reality of chronic pain syndrome can get in the way of your everyday life and activities and often plays a role in developing mental health disorders such as depression or substance use.
There are some chronic pain treatments, but finding the one that works for you can take time.
How Common Is Chronic Pain Syndrome?
- More than 1 in 5 adults experienced chronic pain in the last three months
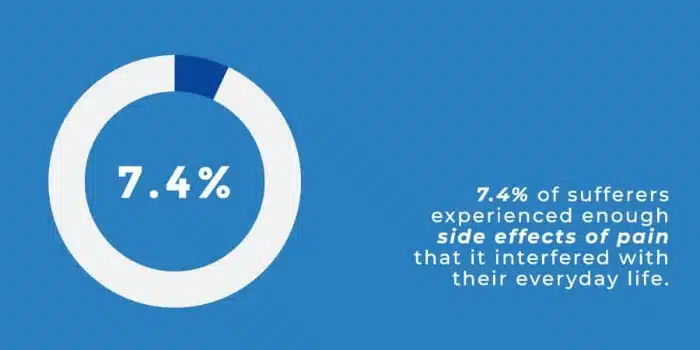
- 7.4% experienced enough side effects of pain that it interfered with their everyday life
- Adults aged 65 and over are the most likely to experience chronic pain
- People who live in rural areas are more likely to experience chronic pain
- Non-Hispanic white adults were the most likely to experience chronic pain
Since chronic pain is so prevalent, work has been done to advance chronic pain therapy, treat chronic pain effectively, and provide people relief from chronic pain.
What Makes You Feel Chronic Pain?
The direct cause of chronic pain also differs between patients. Chronic pain can result from trauma, injury, chemotherapy, infection, or nerve damage.
Chronic Pain: an Inside Look
What Is The Difference Between Chronic Pain and Other Pain?
Symptoms of Chronic Pain Syndrome
Joint Pain
Muscle Aches
Burning Pain
Fatigue
Sleep Problems
Loss of Stamina and Flexibility
Mood Problems
Causes of Chronic Pain Syndrome
Chronic pain has dozens, if not hundreds, of different causes. Sometimes, even the natural aging process can result in conditions that cause chronic pain. Below, we’ve listed some of the most common chronic pain causes to guide chronic pain treatment.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is caused by a progressive wearing down of the tissue found at the ends of bones and can cause substantial joint pain that may become chronic. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and responds to some treatments and medications.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Back Pain
Back pain is one of the most common causes of chronic pain and has several different causes. 4 Back pain may result from repeatedly lifting heavy objects, bulging or ruptured discs, or as a side effect of osteoarthritis. When back pain is a frequent cause of discomfort and distress, it can lead to chronic pain syndrome.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disease with no known cause. It affects roughly 2% of adults in the United States and is characterized by pain felt across the entire body. 5
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Advanced Cancer
Cancer pain is a severe side effect of an intense disease.7 The likelihood that somebody develops chronic pain syndrome due to advanced cancer depends on the individual, the type of cancer, and what stage the cancer has reached. According to recent data, 1 in 3 cancer survivors will also deal with chronic pain.8
How Is Chronic Pain Diagnosed?

- How long have you been experiencing the pain?
- On a scale from 1 to 10, how severe is the pain?
- Where is the pain located?
- Does the pain feel like burning, aching, or pins and needles?
- Does anything trigger the pain?
They may also investigate your medical history to see if you have any risk factors for chronic pain and may be able to help provide treatments for dealing with chronic pain.
What Tests Are Used to Diagnose Chronic Pain?
What Are the Risk Factors for Chronic Pain?
Several risk factors for chronic pain are entirely out of your control. Others are lifestyle factors that could be addressed. The risk factors for chronic pain include:
- Genetics
- Obesity
- Older age
- Having a previous injury
- Having a labor-intensive job
- Experiencing stress
- Smoking
While you can’t change your age or genetics, cutting back on smoking, finding ways to relieve stress, or engaging in healthy eating and exercise practices can reduce your risk of developing chronic pain syndrome.
What Are The Complications of Chronic Pain?

Chronic pain can affect nearly every aspect of your life. Since the pain is so persistent, it can interfere with getting out of the house, seeing friends, or simply feeling comfortable in your own home. Furthermore, the repeated experience of pain can lead to brain adaptations that interfere with motivation and reward.9
Chronic pain can reduce your overall quality of life, lead to depression or anxiety, amplify the effect of existing chronic disease, and put people at an increased risk of suicide. It can also lead to substance use disorders, as people look for any possible mechanism to relieve the symptoms of pain in their everyday life.
And while certain drugs can relieve the effects of pain for a short period, developing an addiction often ends up worsening overall pain. It can also decrease your quality of life.
Answers to Questions Pertaining to Chronic Pain
Can Chronic Pain Be Prevented?
Cutting down on harmful activities like smoking or substance use can further reduce your risk of developing chronic pain syndrome. It also helps to get consistent, quality sleep.
What Is the Prognosis for People with Chronic Pain?
Ultimately, the prognosis for chronic pain patients depends on their specific set of symptoms and medical history. Some people may respond well to treatment and chronic pain therapy, while others may struggle with finding any form of tangible relief.
How Can I Cope with Chronic Pain?
Eat a Healthy Diet
Exercise Regularly
Get Enough Sleep
Manage Your Stress
Limit Alcohol
Treatment for Chronic Pain Syndrome

Physical Therapy
Physical therapy aims to treat chronic pain by correcting muscle imbalances, teaching people strategies to avoid chronic pain triggers, and helping people learn how to exercise despite suffering from chronic pain syndrome.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy might include helping people learn to use ambulatory devices — such as a cane or walker — learning to avoid situations that lead to chronic pain and navigating everyday situations that your chronic pain interferes with.
One-On-One or Group Therapy
Relaxation Techniques Such as Deep Breathing or Meditation
Nerve Blocks
Pain Medicines
NSAIDs, antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs, and muscle relaxants are common medications that people can use to help mitigate chronic pain.
Surgery to Treat the Condition That Caused the Pain
In some cases, surgery can stop chronic pain at the source. People who have a slipped disk and experience chronic back pain, for instance, may benefit from corrective surgery that puts the disk back into place. Not all chronic pain conditions can benefit from surgery but speaking to your doctor about whether surgery is the right choice for you can help you learn about your options.
Our expert team at J. Flowers Health Institute can help not only identify the root of your pain, but alleviate the symptoms. Don’t hesitate to reach out and begin your healing journey.
Managing Chronic Pain: A Deeper Look
Resources
- https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db390.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/osteoarthritis.htm
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353648
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906
- https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/fibromyalgia.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-IBD.htm
- https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/coping/physically/cancer-and-pain-control/causes-and-types
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/article-abstract/2736363
- https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2014/07/study-reveals-brain-mechanism-behind-chronic-pains-sapping-of-mo.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022399909000944?casa_token=Np7ZQ5QYmdcAAAAA:KGZ_oDaaQu9lpXiHQQpL1VeHWcWVR0BksdUvKOaEJ2MG-qVMWGgeuEqOOmBerU6pUYsY429aigg





